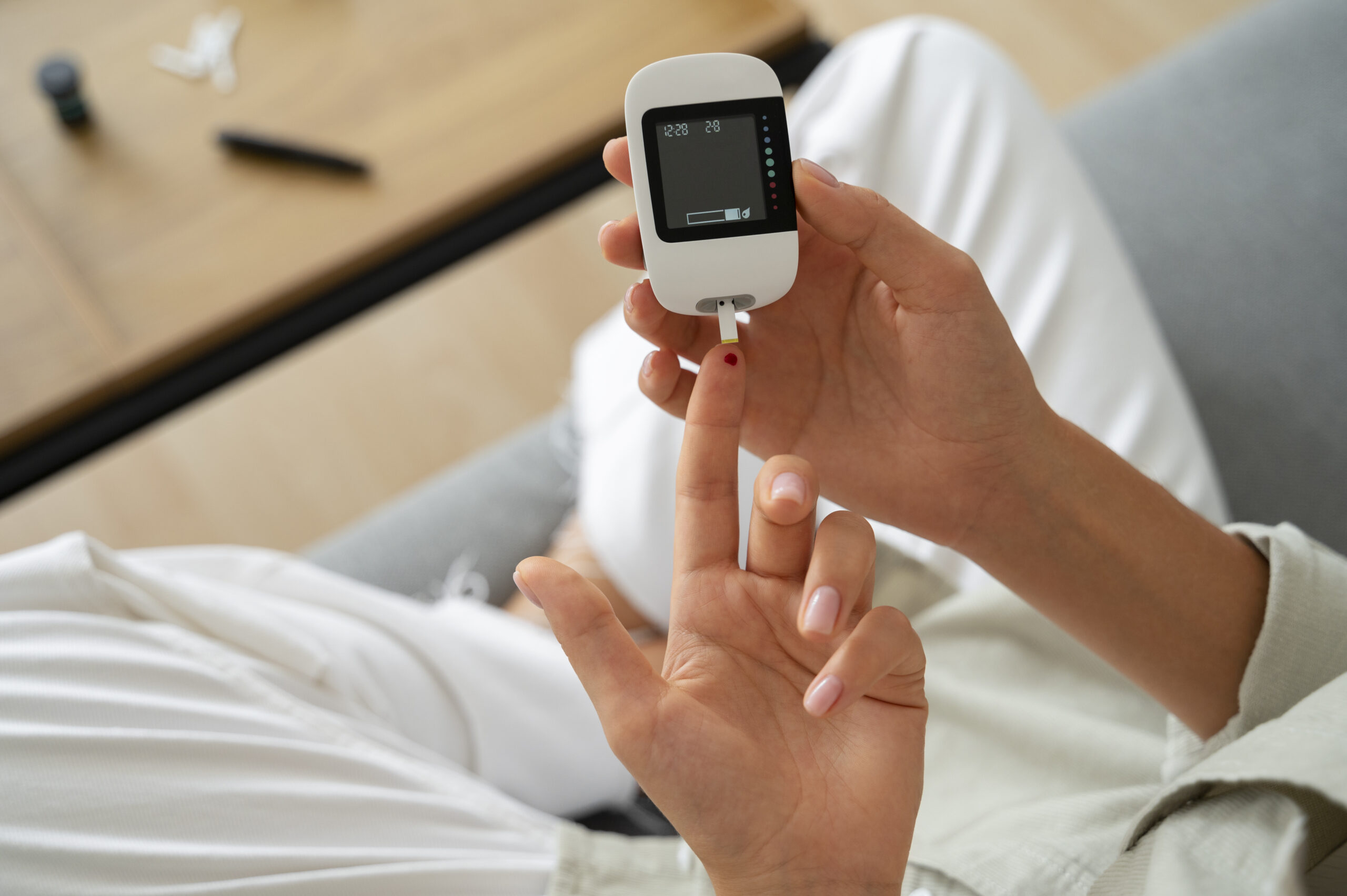
Introduction
A chronic illness that affects millions of individuals globally is diabetes. It is a relentless and often overwhelming diagnosis, but understanding the basics , including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is crucial for effectively managing this condition and leading a healthy life. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of this disease, providing you with valuable insights and information that can help you navigate this challenging journey with confidence and hope.
Table of Contents
What is Diabetes?
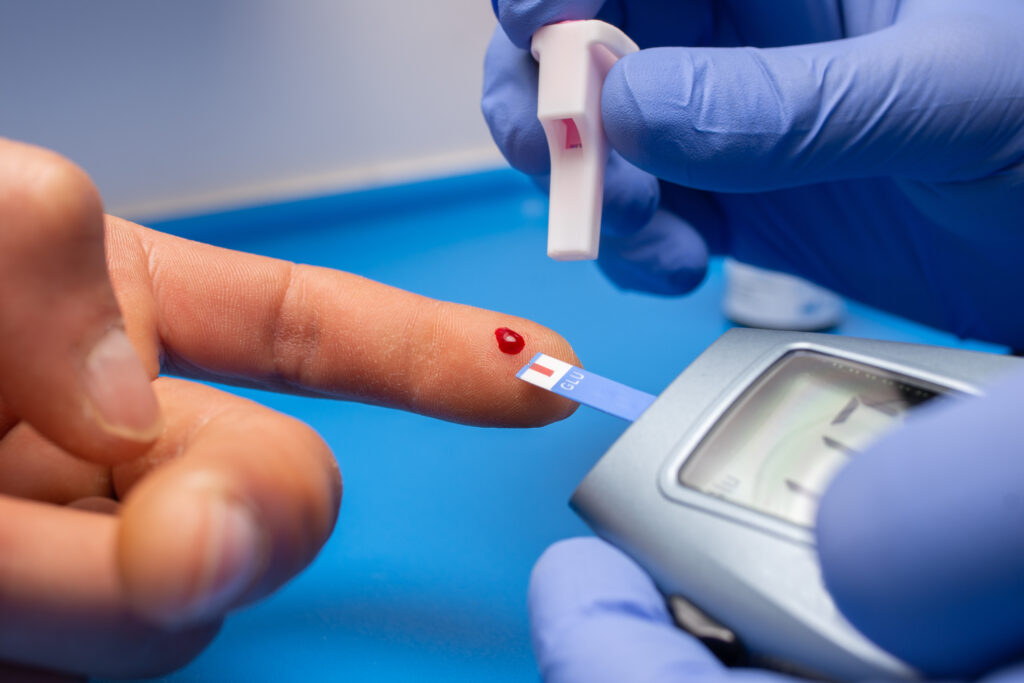
its a metabolic disease marked by increased blood glucose (sugar) levels. This takes place when the body has no capacity to use the insulin it creates, or when it does not produce enough of the hormone that controls blood sugar. Type 1, Type 2 , and gestational are the three main kinds of this disease.
Causes
mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, arises due to a complex interplay of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Understanding the causes involves delving into this three main types.
Type 1 :
Type 1 results from an autoimmune reaction where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas called beta cells. This leads to a deficiency of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. While the exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, such as viral infections, are believed to play significant roles.
Type 2 :
Type 2, the most common form, typically develops gradually over time and is closely linked to lifestyle factors and genetics. Insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin’s effects, is a key characteristic of type 2 . Several factors contribute to insulin resistance, including obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet high in refined carbohydrates and saturated fats, and chronic inflammation. Genetics also play a role, with certain genetic variations increasing susceptibility to type 2 .
Gestational :

The exact cause of gestational is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from hormonal changes and insulin resistance during pregnancy. As pregnancy progresses, the placenta produces hormones that can impair the action of insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. For most women, the pancreas can produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance. However, in some cases, especially when insulin production cannot keep up with increased demand, gestational develops.
Symptoms of this disease are :
Common symptoms includes:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Swelling or tinning in the hands or feet

Living with this can be an emotional rollercoaster, with moments of fear, frustration, and uncertainty. However, recognizing and addressing the symptoms is the first step towards taking control of this condition and leading a healthy life.
Treatment Options
Managing this disease effectively requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication, monitoring, and education.
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight management are essential for managing this. These lifestyle changes can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with this problem.

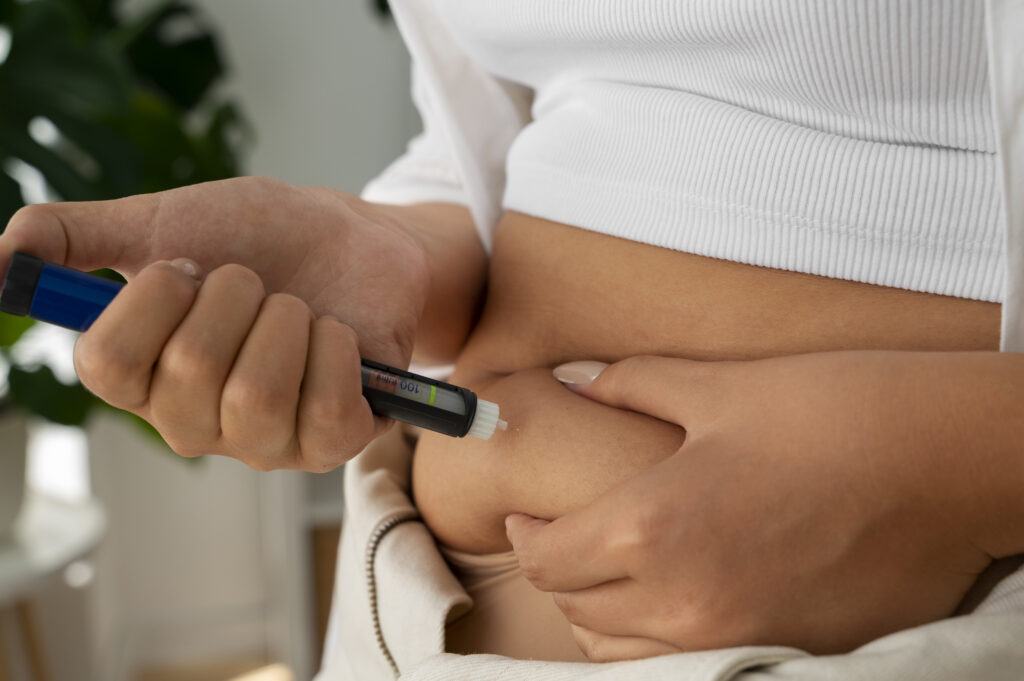
- Medication: Depending on the type of diabetes, medication such as insulin, oral medications, or other injectable drugs may be prescribed. These medications can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with this disease.
- monitoring: To effectively manage this , blood sugar levels have to be constantly examined. Continuous glucose monitoring devices or finger-prick tests can be used for this. .
- Education and Support: education and support from healthcare professionals can help individuals better understand and manage their condition. This can include learning about healthy eating, physical activity, medication management, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics , including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is crucial for effectively managing this condition. By making lifestyle changes, monitoring blood sugar levels, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with this problem can lead a healthy and fulfilling life. Stay informed, stay proactive, and remember that with the right knowledge and support, living well with this is entirely achievable.
Living with this Disease can be challenging, but it is not a death sentence. With the right knowledge, support, and resources, individuals can lead a healthy and fulfilling life. By understanding the basics of this Problem, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of this condition and live a life that is not defined by diabetes but rather enriched by it.
All the images are taken from https://www.freepik.com/
FAQs
How do lifestyle factors contribute to Type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity can lead to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
What is the relationship between obesity and Type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can cause insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Can family history increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes?
c Answer: Yes, having a close relative with Type 2 diabetes can increase an individual’s genetic risk, though lifestyle factors also play a significant role.
Can other medical conditions increase diabetes risk?
Yes, conditions like PCOS, Cushing’s syndrome, and acromegaly can disrupt blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- डिजिटल डिटॉक्स: स्क्रीन टाइम कम करने से तनाव कैसे कम हो सकता है। screen time Can Reduce Stress in hindi.
- Digital Detox: How Lowering Screen Time Can Reduce Stress.
- “Manu Bhaker Aims For Historic Third Medal In 25m Pistol “.
- भाग्य की दौड़: शा’कारी रिचर्डसन पेरिस 2024 सर्ज। Sha’Carri Richardson’s paris surge in hindi.
- Racing To Redemption: Sha’Carri Richardson’s Paris 2024 Surge.



