Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common health condition affecting millions of women worldwide. This hormonal disorder can lead to various symptoms and health complications if not properly managed. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the signs and treatment of PCOS to provide a better understanding of this condition and how to manage it effectively.
Table of Contents
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, commonly known as PCOS, is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens).
Common Signs and Symptoms of PCOS
1. Irregular Periods
One of the most common signs of PCOS is irregular menstrual cycles. Women with PCOS may experience fewer periods (fewer than eight in a year) or have prolonged menstrual cycles that last for more than 35 days. In some cases, women with PCOS may stop having periods altogether.
2. Excess Androgen Levels
High levels of androgens can lead to excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness. These symptoms can be distressing and significantly impact a woman’s self-esteem and quality of life.
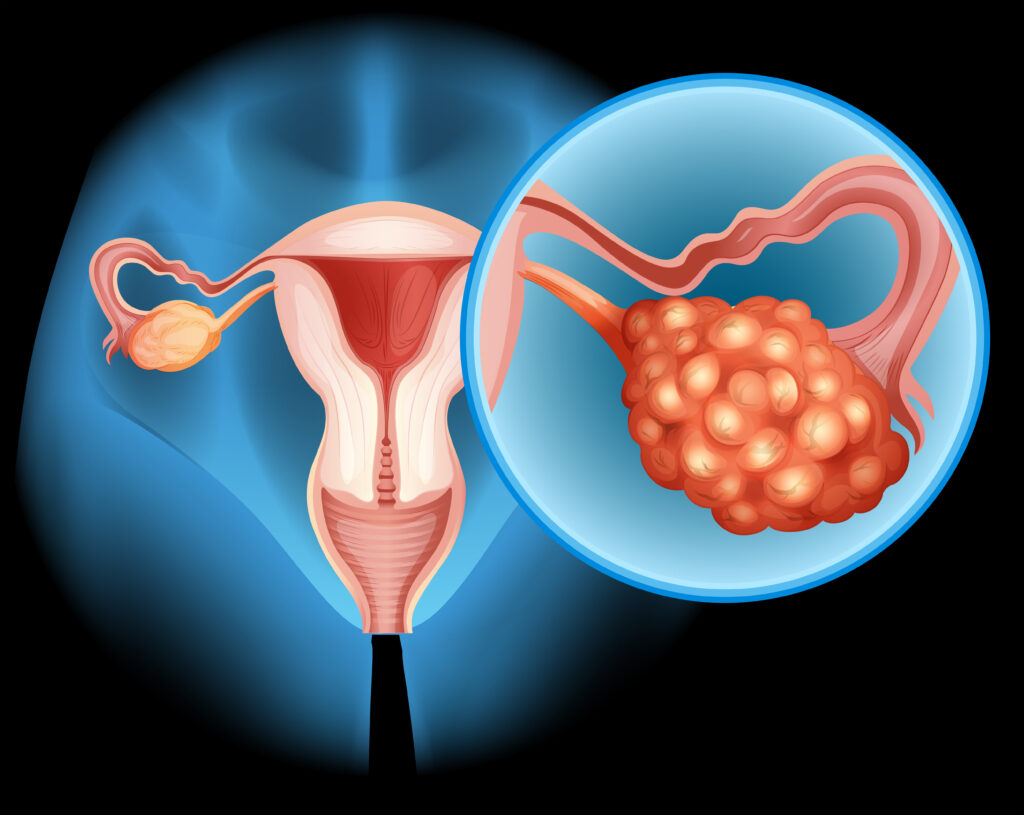
3. Polycystic Ovaries
An ultrasound examination often reveals enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts. These cysts are immature ovarian follicles that fail to release eggs regularly.
4. Weight Gain
Many women with PCOS experience unexplained weight gain or have difficulty losing weight. This weight gain is often concentrated around the abdomen, which can increase the risk of developing other health issues.
5. Insulin Resistance
PCOS is commonly associated with insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This can lead to higher levels of insulin in the blood, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
6. Infertility
Infertility is a significant concern for many women with PCOS. The hormonal imbalances and irregular ovulation associated with PCOS can make it challenging to conceive without medical intervention. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3737989/)

7. Skin Issues
Skin conditions such as darkening of the skin (acanthosis nigricans), skin tags, and severe acne are also common in women with PCOS.
Diagnosing PCOS
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing PCOS typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your healthcare provider will ask about your menstrual cycle, weight changes, and symptoms such as acne and excess hair growth.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests are performed to measure hormone levels, including androgens, insulin, and other relevant hormones. These tests help rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
3. Ultrasound
An ultrasound is used to examine the ovaries for the presence of cysts and to check the thickness of the endometrium (lining of the uterus).
4. Additional Tests
In some cases, additional tests such as glucose tolerance tests and lipid profiles may be recommended to assess the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Understanding the Causes of PCOS
1. Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in the development of PCOS. If your mother or sister has PCOS, your chances of developing the condition are higher.
2. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a common feature of PCOS. High insulin levels can lead to increased androgen production, which can interfere with the development of ovarian follicles and ovulation.
3. Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation is also associated with PCOS. Women with PCOS often have higher levels of inflammatory markers, which can contribute to insulin resistance and other symptoms.
Treatment Options for PCOS
1. Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications are often the first line of treatment for managing PCOS symptoms. These changes can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being.
Diet
A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage insulin levels and promote weight loss. Reducing the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates is also beneficial.
Exercise
Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, aid in weight management, and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety associated with PCOS. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
2. Medications
Several medications can help manage PCOS symptoms and improve quality of life.
Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal birth control pills are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and manage acne and excessive hair growth.
Metformin
Metformin is a medication used to treat insulin resistance and lower blood sugar levels. It can also help with weight loss and restoring regular menstrual cycles.
Anti-Androgens
Anti-androgen medications such as spironolactone can help reduce excessive hair growth and acne by blocking the effects of androgens.
3. Fertility Treatments
For women struggling with infertility, several treatment options are available.
Clomiphene Citrate
Clomiphene citrate is an oral medication that stimulates ovulation and increases the chances of conception.
Letrozole
Letrozole is another medication that can induce ovulation and is often used in women who do not respond to clomiphene citrate.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies can be considered if other treatments are unsuccessful.
4. Surgical Options
In some cases, surgical interventions may be recommended.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can trigger ovulation in women who do not respond to medication.
Managing PCOS Through Holistic Approaches
1. Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate PCOS symptoms. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
2. Sleep Hygiene
Quality sleep is crucial for hormonal balance. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a restful sleep environment can improve sleep quality and reduce PCOS symptoms.
3. Herbal Remedies
Some women find relief from PCOS symptoms through herbal remedies. While more research is needed, herbs like cinnamon, spearmint tea, and inositol supplements may have beneficial effects.

Long-Term Health Implications of PCOS
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease due to factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
The insulin resistance associated with PCOS increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate this risk.
3. Endometrial Cancer
Irregular menstrual cycles and prolonged periods without ovulation can increase the risk of endometrial cancer. Regular monitoring and treatment to regulate menstrual cycles can help reduce this risk.
4. Mental Health
PCOS can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and eating disorders. Seeking support from mental health professionals and joining support groups can be beneficial.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. Understanding the signs and symptoms of PCOS is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. By adopting healthy lifestyle changes, utilizing appropriate medical treatments, and exploring holistic approaches, women with PCOS can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Regular monitoring and working closely with healthcare providers are essential for addressing the long-term health implications associated with PCOS. Remember, every woman’s experience with PCOS is unique, and finding the right combination of treatments may take time and patience.
picture taken from https://www.freepik.com/
FAQ
What causes PCOS?
PCOS is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, elevated levels of androgens, and chronic inflammation are commonly associated with PCOS
Can PCOS be cured?
There is no cure for PCOS, but the symptoms can be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, medications, and other treatments. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for reducing the risk of long-term health complications.
Is it possible to get pregnant with PCOS?
Yes, many women with PCOS can get pregnant, though they may need medical interventions to help with ovulation. Treatments such as clomiphene citrate, letrozole, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like IVF can increase the chances of conception



